smartbuildingmag.com
12
'23
Written on Modified on
MEDIAWORLD
Energy Efficient Systems – why do we need it so much?
Many of you might think that energy-efficient systems in the building are a now-days situation, cost a lot of money, and need massive reconstruction… I deeply apologize, but I have to prove you wrong! Written by Maria Brueva.

Image source: ABB the Energy Efficiency Movement
Energy-efficient systems in smart buildings refer to technologies and strategies designed to optimize energy consumption and reduce wastage while maintaining a comfortable and productive indoor environment. These systems integrate advanced technologies, automation, and data analytics to monitor, control, and manage various building systems effectively.
The use of energy-efficient systems in buildings can be traced back to various points in history, but it gained more significant momentum in the latter half of the 20th century and continues to evolve to this day. Here are some key milestones and periods of progress in the adoption of energy-efficient systems in buildings:
Energy-efficient systems in smart buildings refer to technologies and strategies designed to optimize energy consumption and reduce wastage while maintaining a comfortable and productive indoor environment. These systems integrate advanced technologies, automation, and data analytics to monitor, control, and manage various building systems effectively.
The use of energy-efficient systems in buildings can be traced back to various points in history, but it gained more significant momentum in the latter half of the 20th century and continues to evolve to this day. Here are some key milestones and periods of progress in the adoption of energy-efficient systems in buildings:
- 1970s-1980s: The oil crises of the 1970s raised awareness about energy dependence and the need for conservation. During this period, energy-efficient building design concepts, such as passive solar design and better insulation, gained attention. The focus was on reducing energy consumption through better building materials and designs.
- 1990s: In the 1990s, with advancements in technology and growing environmental concerns, more sophisticated energy-efficient systems started to emerge. Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS) became more prevalent, allowing centralized control and monitoring of HVAC, lighting, and other building systems.
- 2000s: The early 2000s saw increased interest in green building standards and certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), which promoted sustainable building practices, including the use of energy-efficient technologies.
- 2008-2009: The global financial crisis led to a renewed emphasis on energy efficiency as a means to reduce operating costs for businesses and governments. Energy-efficient retrofits and upgrades gained popularity during this time.
- 2010s: The 2010s witnessed rapid advancements in technology, particularly in the fields of automation, data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These innovations facilitated the development of smart building systems, which optimized energy usage based on real-time data and occupant behaviour.
- Present: Government Regulations and Incentives, in many countries, governments began introducing regulations and providing incentives to encourage the adoption of energy-efficient systems in buildings. These policies aimed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, combat climate change, and promote sustainable development. A massive interest in Renewable Energy: The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into buildings became more practical and affordable. This allowed for onsite generation of clean energy, further enhancing the energy efficiency of buildings.
- Future: Energy-efficient systems in buildings continue to advance as technology evolves and sustainability becomes a higher priority worldwide. Machine learning, artificial intelligence, and more sophisticated automation are expected to further optimize energy usage and enhance building efficiency.
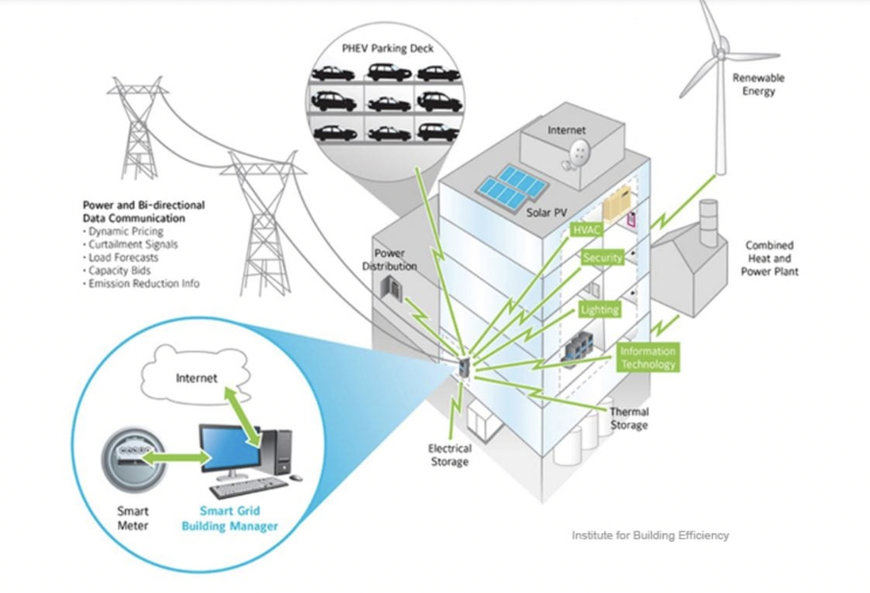
Image source: Institute for Business Efficiency
Today, energy-efficient systems are considered standard practice in modern building design and construction. As the world continues to tackle climate change and strive for a more sustainable future, the development and adoption of energy-efficient systems will likely remain a crucial aspect of building design and operation.
Here are some examples of energy-efficient systems commonly found in smart buildings of nowadays:
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) Systems: Smart buildings employ intelligent HVAC systems that use sensors and data analytics to adjust heating, cooling, and ventilation based on real-time occupancy, outdoor weather conditions, and indoor temperature preferences. This helps in avoiding energy waste and maintaining optimal comfort levels.
Lighting Systems: Energy-efficient lighting systems utilize LED technology and automated controls to adjust lighting levels based on occupancy and natural light availability. Occupancy sensors, daylight harvesting, and scheduled lighting are some common features that reduce energy consumption in lighting.
Building Envelope: The building envelope refers to the outer shell of the building, including walls, windows, roofs, and insulation. Energy-efficient smart buildings use high-performance materials and insulation to minimize heat gain or loss, thus reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
Renewable Energy Integration: Smart buildings often incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines to generate electricity on-site. These renewable energy systems can power some of the building's energy needs, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources and lowering carbon emissions.
Energy Management Systems (EMS): EMS provides centralized control and monitoring of energy-consuming systems in the building. It collects data from various sensors and devices, analyzes energy usage patterns, and optimizes energy consumption based on the building's requirements and external factors.
Occupancy and Space Utilization Sensors: These sensors detect the presence of occupants in different areas of the building and adjust lighting, HVAC, and other systems accordingly. When a room is unoccupied, the system can automatically adjust settings or even switch off equipment to save energy.
Smart Grid Integration: Smart buildings can interact with the smart grid to optimize energy usage based on electricity pricing and demand patterns. They can shift energy-intensive tasks to off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper and the grid is less burdened.
Water Management Systems: These systems help in efficient water usage by monitoring consumption, detecting leaks, and controlling water flow in plumbing fixtures and irrigation systems.
Intelligent Building Controls: Smart buildings utilize advanced building automation and control systems that analyze data from various sensors and make intelligent decisions to optimize energy use, occupant comfort, and operational efficiency.
Demand Response Strategies: Smart buildings can participate in demand response programs, where they reduce energy usage during peak demand periods to support grid stability and earn incentives.
Let us take a look at some of the main companies that have been recognized for their contributions to energy-efficient systems and their latest innovations in the field:
Siemens: Siemens is a global technology company that offers a wide range of products and solutions for building automation, energy management, and smart grid integration. They provide energy-efficient HVAC systems, lighting controls, and building automation solutions. Siemens has presented a Siemens Xcelerator is an open digital business platform that enables customers to accelerate their digital transformation easier, faster and at scale. Together with their Energy Efficiency Drive, which electric motors account for 70 % of the total industrial electrical energy demand. Improving the energy efficiency and energy productivity based on a comprehensive drive system approach make a significant contribution to a sustainable future.
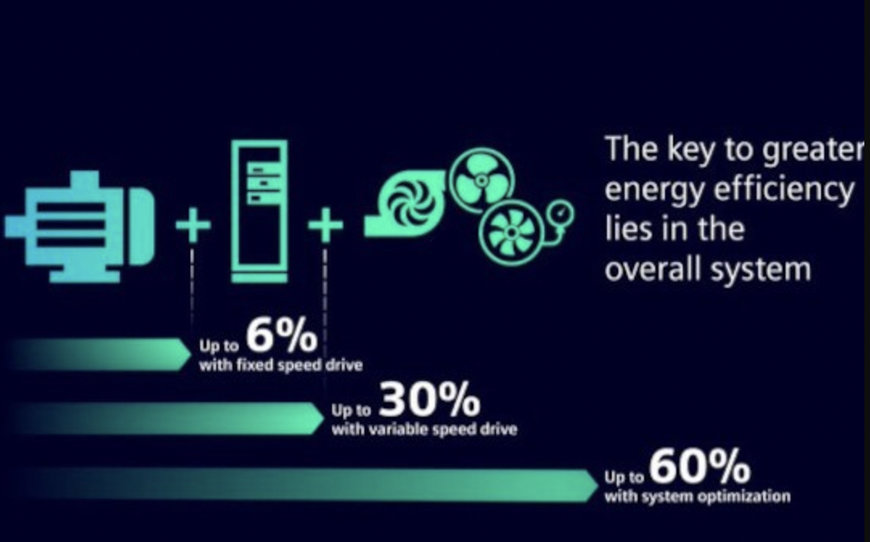
Image source: Siemens, Energy-efficient drive systems
Schneider Electric: Schneider Electric is a leading provider of energy management and automation solutions. They offer a variety of products and services for energy-efficient buildings, including building automation, lighting controls, and renewable energy solutions. Schneider Electric presented EcoStruxureTM to achieve greater energy performance and sustainability with smart power distribution systems integrating energy management software that accurately tracks and analyses their electrical energy usage in commercial and private buildings.
Honeywell: Honeywell provides energy-efficient building solutions, including HVAC controls, building automation systems, and energy management software. Honeywell develop and deploy the most advanced technologies to serve energy and industrial companies looking for more profitable, reliable and cleaner solutions. Our diverse portfolio of technologies and solutions are helping organizations reach their environmental, social and governance goals, and shaping the path and pace of the energy transition.
ABB: ABB is a multinational corporation known for its expertise in power and automation technologies. They offer energy-efficient building solutions, including smart building automation systems and energy management solutions. ABB developed a wide portfolio of fit-for-purpose low and medium voltage AC and DC variable speed drives. They control the speed and torque of motors that could increase energy efficiency up to 80%.
Trane Technologies: Trane Technologies is a global climate control solutions provider offering energy-efficient HVAC systems and building automation solutions. We’re continually faced with energy consumption challenges as you try to create pleasing indoor spaces, navigate costs that impact bottom lines and plan greenhouse gas reduction initiatives. Trane’s consultative approach offers cross-functional, beginning-to-end building expertise that transforms the way we engage with energy.
Eaton: Eaton provides a wide range of power management solutions, including energy-efficient lighting systems, building automation, and electrical distribution products. Eaton has proposed a full range of products to help cut the bills and reduce CO2. Everything as a Grid is our approach to reinventing the way power is distributed, stored and consumed. Our Everything as a Grid approach is shaping a future where homeowners and businesses can reduce the cost and environmental impact of energy. Flexible, intelligent power creates new opportunities for everyone.
The transition to a more sustainable, low-carbon future is accelerating. This energy transition is driven by the progressive replacement of carbon-based fuels with renewables, clean air regulation and the direct and indirect electrification of more applications. The companies mentioned above have demonstrated a commitment to developing and promoting energy-efficient systems that help reduce energy consumption, lower operating costs, and contribute to sustainability in the building sector. Keep in mind that the industry is dynamic, and there might be other emerging companies and startups that are also making significant strides in energy-efficient systems.
Conclusion
Energy efficiency is essential for several compelling reasons, and its significance continues to grow as we face global challenges related to energy consumption and environmental sustainability. Here are some key reasons why energy efficiency is crucial, like
Environmental benefits, where energy efficiency helps reduce the demand for energy, which, in turn, leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions and other harmful pollutants associated with energy production. By using less energy to achieve the same outcomes, we can mitigate the impact of climate change, air pollution, and water pollution.
Resource Conservation, as we know many energy sources, such as fossil fuels, are finite and non-renewable. By improving energy efficiency, we can make the most of our limited resources and extend the lifespan of these resources, reducing our dependence on them, which will bring us towards our sustainable goals:
- Cost Savings: Energy-efficient technologies and practices help lower energy consumption, leading to reduced energy bills for consumers and businesses. By investing in energy efficiency, individuals and organizations can save money in the long run.
- Sustainable Economic Growth: Energy efficiency can drive economic growth by stimulating innovation and creating jobs in the clean energy sector. It promotes sustainable development by balancing economic prosperity with environmental protection.
- Building Resilience: Energy-efficient buildings and infrastructure are often more resilient to power outages and extreme weather events, as they rely on alternative energy sources and are designed to conserve energy.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Energy efficiency directly contributes to reducing an individual's or organization's carbon footprint. By using energy more wisely, we can collectively work towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Overall, energy-efficient systems in smart buildings contribute to significant cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and improved occupant comfort and productivity. They are an essential aspect of sustainable and future-ready construction practices. Energy efficiency is a fundamental pillar of sustainable development and climate action. It empowers us to use resources wisely, protect the environment, and create a more secure and prosperous future for generations to come.
References
References
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-020-00582-3
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7822355
- https://www.usgbc.org/leed
- https://smartbuildingmag.com/news/68658-energy-saving-in-smart-buildings
- https://marketplace.siemens.com/global/en/all-offerings/solutions/e/energy-efficient-drive-systems.html
- https://new.abb.com/news/detail/104992/update-on-the-energy-efficiency-movement
- https://www.siemens.com/global/en/products/drives/topic-areas/energy-efficiency.html

